Blog ENG
News and trends in the world of data science
In a previous blog post about recent news in the world of data science, we wrote about Deepfakes and DeepMind’s Ithaca, a tool that in a way deals with predicting events in the past. This time we will once again talk about a tool developed by DeepMind that is currently being debated as to whether we are on the verge of developing the first system of artificial general intelligence. To understand what artificial general intelligence is all about, we will give some definitions and an introduction about the types of artificial intelligence.
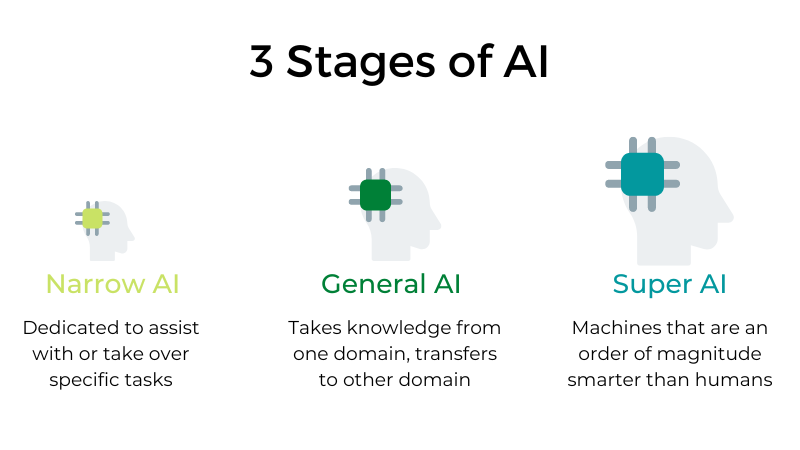
Artificial Narrow Intelligence
I believe that we are all already very familiar with the concept and meaning of Artificial Intelligence (AI). But there are several types of artificial intelligence, and it is very likely that when we say artificial intelligence, we mean the simplest, narrow artificial intelligence (ANI). ANI represents AI-based systems that we know today and that are specified to solve one problem or to solve several problems but from the same domain and can perform individual, automated and repetitive tasks. Thus, they are specifically designed and taught to solve a particular type of problem and do not need to have general cognitive abilities.
By definition, they have narrow possibilities, such as recommending content to the user of an e-platform or predicting the demand for certain products. This is the only type of artificial intelligence that exists today. Systems based on this type of AI can approach human functioning and thinking in very specific contexts, and even surpass them in many cases, but stand out only in highly controlled environments with a limited set of parameters.
Artificial General Intelligence
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is the ability of an intelligent agent or system to understand or learn any intellectual task that a human being can understand. It is still only a theoretical concept and the primary goal of some artificial intelligence research as well as a common topic in science fiction and future studies. AGI is defined as AI that has cognitive functions at the human level, in a wide range of domains such as language processing, image processing, computer functioning and thinking, etc. In theory, an AGI system should consist of thousands and thousands of ANI systems operating in a team communicating with each other to mimic human thinking and act accordingly. In simpler words, the goal of AGI is to create machines that would be able to understand the world with the same capacity as any human being and based on these external inputs have the ability to discover solutions to a given problem.
However, even with the most advanced computer systems and infrastructures, such as Fujitsu’s K or IBM’s Watson, it currently takes about 40 minutes to simulate one second of neural activity. This speaks to the enormous complexity and interconnectedness of the human brain but also to the magnitude of the challenge of building an AGI with the resources currently available to us.
Artificial Super Intelligence
Here we are almost entering the territory of science fiction, but Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) is considered a logical advance and continuation of AGI. An artificial super intelligence system could surpass all human capabilities. This would involve solving problems in terms of making rational decisions and even things like making better art and building emotional relationships. Once and if we achieve general artificial intelligence, artificial intelligence systems could quickly improve their capabilities and advance into areas we may not have even dreamed of. Although the gap between AGI and ASI would be relatively narrow (some say only nanoseconds, because artificial intelligence would learn so quickly), the long journey ahead of us towards AGI itself makes this seem like a concept that lies far away in the future.
Gato
In a paper published in May this year, DeepMind presented Gato, which is closer to AGI than anything that has been made and seen so far. Gato can learn to play Atari games, generate realistic text, process images, stack colorful blocks using a robotic arm and more. Gato is able to perform more than 600 different tasks and all with the same neural network with the same weights.
The architecture of Gato is not so different from the architecture of many AI systems used today. Although the architecture of Gato is not described in detail in the paper, it is clear that it is based on transformers that are used to process natural language and generate text. You can read more about transformers and their architecture in one of our past blog posts. Inspired by large language models, DeepMind has taken a similar approach, but has expanded its field of activity beyond the field of text output. Gato operates as a multimodal, multi-task, multi-embodied network, meaning that the same network (i.e., one architecture with one set of weights) can perform a large number of different tasks, despite involving inherently different types of inputs and outputs.
Gato’s design is based on the principle of training on the widest possible range of relevant data such as images, text, proprioception, joint torques, button presses and other discrete and continuous observations and actions. For simulated control tasks, Gato is trained on datasets generated by state-of-the-art reinforced learning agents trained in a range of different environments. In terms of visual and textual data, Gato is trained on the MassiveText dataset, a collection of large textual datasets in English from a variety of sources: websites, books, newspaper articles and source code.
There are also several datasets that are a combination of textual and visual data, such as ALIGN, which consists of 1.8 billion images with alt text annotation used within HTML code to describe the appearance and function of a particular image.
In addition, the fact that Gato is not even close to the largest neural networks we have seen so far is quite impressive. With its 1.18 billion parameters, we can compare it to the GPT-2 language model created by OpenAI in 2019 and it is even 2 orders of magnitude smaller than their GPT-3 model.
Currently, expert opinions on whether Gato is indeed the first, primitive representative of AGI are divided. One of the authors of Gato, Nando de Freitas, said on Twitter that the creation of general artificial intelligence is no longer science fiction, but it is possible to make artificial intelligence bigger and more efficient, it just needs to be given enough data. On the other hand, Gary Marcus from the American company Robust.AI, believes that the situation is not as simple as it might seem at first glance and that Gato has learned to do each of its tasks, but when faced with new challenges, it will not be able to logically analyze and solve.
While there is debate among experts as to whether we are witnessing the creation of the first AGI, most agree that Gato’s potential is unquestionable, but it remains to be seen whether this is indeed a forerunner of general artificial intelligence and a stepping stone for AGI development or just another ANI model but trained on a very diverse dataset.

